News
Raktayamari Thangka: A Closer Look at the Thangka Worth $45 Million
Overlook
Widely recognised as one of the most important Asian works of art and one of the world’s great textile treasures, this Thangka was recently bought for $45 million.
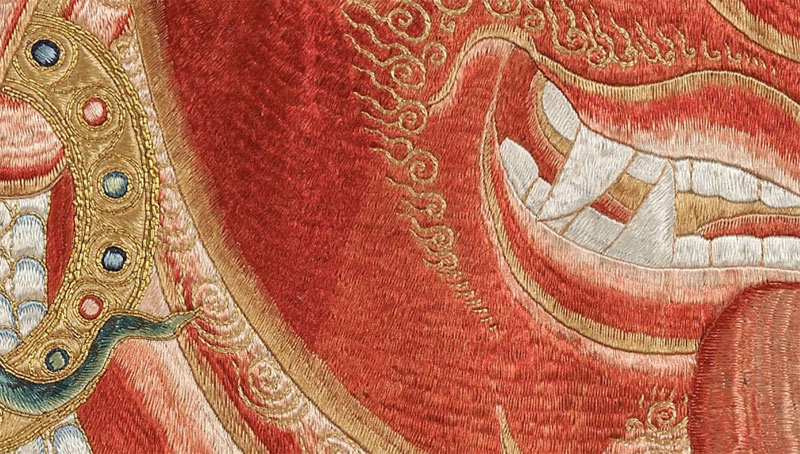


The Thangka depicts the majestic Raktayamari, the red Conqueror of Death, standing in yab-yum embracing his consort, Vajravetali.
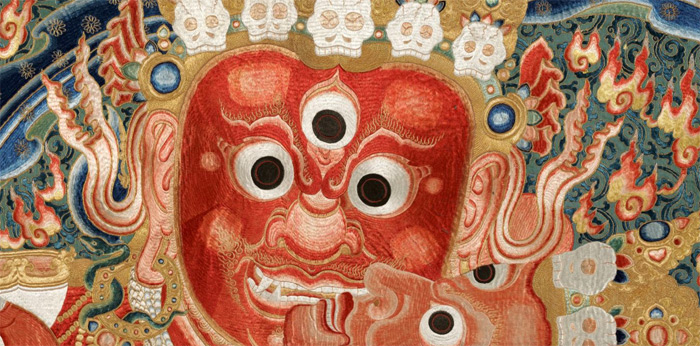
Raktayamari is an important deity of Anuttarayoga-Tantra in Vajrayana Buddhism, and one of the three Yamari forms of Bodhisattva Manjusri (the other two being Vajrabhairava and Krishna-Yamari) revered by various Tibetan sects.
The highlights on the torsos and limbs of Raktayamari and Vajravetali, to denote the musculature, are some of the most common motifs in Nepalese-Tibetan paintings and a notable characteristic of figures in classical Tibetan art.
Highlights and Symbolism
Every aspect of the form of Yamari and the consort Vajra Vetali have symbolic and coded meaning.
The red body color represents the desire to overcome all sufferings and place all beings in the state of enlightenment. The weapon that Raktayamari holds subdues the afflictions (maras).

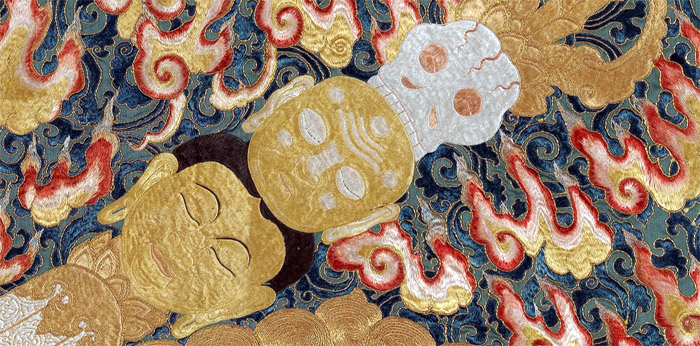
The left hand holds a cup made by ancient Lama’s skull and containing the essence of the four maras transformed.

The three round eyes express compassion for all beings in the three times of past, present and future as well as the three watches of the day and three watches of the night.
The orange and red hair is to symbolize the increasing qualities of the Buddha and the aspects of the Mahayana Five Paths.
The crown of five dry skulls symbolizes the five poisons transformed into the five wisdoms.
The necklace of fifty fresh heads represents the vowels and consonants of the Sanskrit language.

The eight snakes represent the subjugation of various obstacles and the accomplishment of skillful activities.

The locked couple is trampling on the blue corpse of Yama, the Lord of death, wearing a tiger skin and crown, lying on the back of their mount, a brown buffalo recumbent on a multi-coloured lotus base.

All below two rows of buddhas and bodhisattvas seated on lotus bases, the upper including Heruka Vajrabhairava on the far left and Manjusri on the far right, flanking the five Dhyani Buddhas.



Below this row of deities are two Taras – Green Tara on the left, and White Tara on the right.


In the lower panel is a row of seven offering goddesses dancing on lotus bases and holding aloft dishes as offerings below the couple.

Meaning of the artwork
The metaphor for Rakta Yamari is ‘death.’ The name means the ‘Red Killer of Death.’
In this symbolic meaning the idea of death refers directly to the suffering and unhappiness in the world as described in Buddhist philosophy.
The general appearance of the deity, number of faces, arms, ornaments, decorations and attributes are all part of a mnemonic device (memory system) that incorporates the most essential of Buddhist principles and core teachings into a single object.
The one face represents the embodiment of the wisdom of all Buddhas as having one taste, or flavor, ultimate truth. The red body color represents the desire to overcome all “maras” and place all beings in the state of enlightenment.
Bibilography
Henss, Michael. ‘The Woven Image: Tibeto-Chinese Textile Thangkas of the Yuan and Early Ming Dynatsies’, Orientations, November 1997.
Himalayan Art Resources. Rakta Yamari Main Page. http://www.himalayanart.org/search/set.cfm?setID=349. Jeff Watt, 2-2005.
Himalayan Art Resources. Rakta Yamari Textile. HAR no. 57041. http://www.himalayanart.org/image.cfm/57041.html.
Raktayamari-tantraraja-nama. Gshin rje’i gshed dmar po zhes bya ba’i rgyud kyi rgyal po [TBRC w25383, w25384].
Reynolds, Valrae, ‘Buddhist Silk Textiles: Evidence for Patronage and Ritual Practice in China and Tibet.’ Orientations, April 1997.
George Roerich (trans.), Biography of Dharmasvamin, A Tibetan Monk Pilgrim. Patna: K.P. Jayaswal Research Institute, 1959.
George Roerich (trans.), The Blue Annals. Delhi: Motilal Banarsidas, 1996, 2nd ed.
Follow traditionalartofnepal.com on WordPress.com
How To Order
- Browse our catalog and choose your favorite design.
- Select your preferred size and quality to check the price.
- Click on “Product Inquiry” to send us a message and we will check if we the artwork is immediately available. If not we will make it for you.
- Use the cart page to calculate the shipping cost by selecting your country.
- Once we receive your order we will start creating the artwork according to your preferences and provide you with updates and images upon your request.
We strive to ensure a smooth shopping experience with our assistance. We also welcome commissions of custom designs of thangkas, masks and mandalas.
Shipping and Payments
We offer trusted shipping options to ensure your purchases arrive in perfect condition, and delivered in 5 to 10 working days worldwide. We accept PayPal, debit/credit cards and bank wire transfer services.
About Our Community
We live in Changunarayan, a UNESCO heritage site located on a forested hill overlooking Bhaktapur and the Kathmandu valley. You are welcome to visit our art school and meet our community of artists and artisans.
Learn More About Our Thangka School And Workshops
 Ganesh Mask Design #01
Ganesh Mask Design #01  Five Jambhala Thangka
Five Jambhala Thangka  Red Mahakala Mask
Red Mahakala Mask  Quan Yin Thangka
Quan Yin Thangka  Vajrabhairava
Vajrabhairava  Sadhu Baba Masks
Sadhu Baba Masks  Universe Om Mandala
Universe Om Mandala